Types Of Computer Processor In The World
- Embedded processor
- Dual core CPU
- Single core
- Digital signal processor
- Microprocessor
- Quad-core CPU
- Qualcomm Snapdragon
- Deca core
- Hexa core
- Microcontroller
- Celeron
- Graphics processing unit
- Pentium
A Look Inside the Processor
- What is inside the processor?
- What does it look like inside CPU?
- What is Intel inside processor?
- What is the memory inside the processor?
- How a processor works?
- Does a processor have memory?
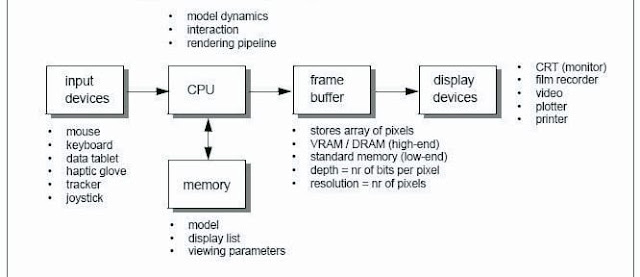
You have already seen how a PC processes and moves data. For most people, the great mystery of the PC is what takes place inside its circuitry.
How can this box of chips, wires, and other parts-most of which don't even move-do its work?
A processor's performance even its capability to function is dictated by its internal design, or architecture. A chip's architecture determines where its parts are located and connected, how it connects with other parts of the computer, and much more. It also determines the path that electricity (in the form of moving electrons) takes as it moves through the processor, turning its transistors on and off. There are many different chip architectures in use today, and each family of PC processors is based on its own unique architecture.
In fact, processors are differentiated by their architecture. The processors of IBM PCs and Macintosh computers have such different architectures, for example, that they cannot even run the same software; operating systems and programs must be written to run on each processor's specific architecture, to meet its requirements.
A processor's architecture determines how many transistors it has, and there fore the processor's power. Simply stated, the more transistors in a processor, the more powerful it is. The earliest microprocessors had a few theusand transistors. The processors in today's PCs contain tens of millions. In the most powerful workstation and server computers, a processor may contain. hundreds of millions of transistors When a computer is configured to use multiple processors, it can ultimately contain billions of transistors.
A processor includes many other features that affect its performance For example, a processor's performance is affected by the number of bits of data it can process at any one time. Currently, nearly all standard PC processors move data in 32-bit chunks, they are called "32-bit processors In 2003 American Micro Devices (AMD) released a new generation of desktop PC processor that) can handle 64 bits of data. (High-end workstations and many minicomputer systems have used 64-bit processors for about a decade.)
Microcomputer Processors
- Which is known as micro processor?
- What are 5 examples of micro computer?
- What is a micro processor in a laptop?
- How many CPU does a micro computer have?
- What is 8 CPUs?
- What is the smallest computer processor?
For two decades after the birth of the personal computer, the biggest player in the PC CPU market was Intel Corporation. This dominance began to change in 1998 when several leading computer makers began offering lower- priced systems using chips made by AMD and other chip manufacturers. Ininally, these microprocessors offered less performance at a lower price. That situation has changed, however, as AMD made rapid advances in its products' capabilities. Today, Intel and AMD chips compete head to head, not only in performance, but also in price.
Intel and AMD are not the only manufacturers on the block. Motorola, now known as Freescale, manufactured the processors for all Macintosh computers up to and including the G4. They still make chips for communication devices. The newer Macintosh GS boasts a chip made by IBM. Many other companies make specialized processors for workstations, minicomputers, handheld devices, automobile electronics, and kitchen appliances.
As you read the following sections, remember that performance specifications and features can change rapidly. Chip manufacturers make constant improvements to their products, as a result, the most popular PC processors now operate at speeds higher than 3 GHz, and they continue to be faster every month. By continuously refining chip designs and manufacturing processes, chip makers are always finding ways to add more transistors to chips.
Intel Processors
- What are the levels of Intel processors?
- Is i7 better than i5?
- How many processors are in Intel?
- What is the most powerful Intel processor?
- What does i3 i5 i7 i9 mean?
- What does i3 i5 i7 mean?
Intel is historically the leading provider of chips for PCs. In 1971, Intel invented the microprocessor-the so-called computer on a chip-with the 4004 model. This invention led to the first microcomputers that began appearing in 1975. Even so, Intel's success in this market was not guaranteed until 1981 when IBM released the first IBM PC, which was based on an Intel microprocessor. A list of current Intel chips, along with their clock speeds and numbers of transistors. microprocessor the Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) Processors
In 1998, Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) emerged as a primary competitor to Intel's dominance in the IBM-compatible PC market. Until that time, AMD processors were typically found in lower performance, low priced home and small business computers selling for less than $1,000 With the release of the K6 and Athlon processor series, AMD proved that it could compete feature for feature with many of Intel's best selling products AMD even began a new race for the fastest PC processor. A list of current AMD chips , along with their clock speeds and numbers of transistors. home Freescale Processors.
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc, a subsidiary of Motorola, Inc., has a 50-year his tory in microelectronics. As mentioned earlier, many Apple computers use Freescale processors. Freescale processors were also an early favorite among companies that built larger, UNIX-based computers.
Through the years, Freescale offered two processor architectures that were used in Macintosh computers. The first is known as the 680x0 family A new type of processor, which was developed by Freescale, Apple, and IBM, has re- placed this family of processors. This new processor architecture, called the PowerPC architecture, is the basis for all new computers made by Apple. Freescale's MPC74xx processors can be found in Apple's G4 computers. PowerPC processors from Freescale are also ideal for Linux operating system implementations, which are growing in popularity among desktop users.
IBM Processors
- Does IBM make processors?
- Which processor is used in IBM?
- What is the difference between Intel and IBM processors?
- What is the full form of IBM in microprocessor?
- What IBM means?
- What do IBM stand for?
In addition to working with Apple and Freescale on the PowerPC line, (BM makes high- performance mainframe and workstation CPUs. In 2003, IBM partnered with Apple and released the GS, advertised as the "fastest desktop processor ever." While most new chips can make this claim, the GS delivered. The G5 delivered true workstation power at the cost of a standard desktop. As a demonstration, Pixar studios were provided with several GS-equipped computers. The Disney/Pixar movie Finding Nemo was created entirely on the G5 desktop computers. Previous releases from Pixar, including Toy Story, required high-end workstations.
Comparing Processors
- How do I compare computer processors?
- How do you compare the performance of two processors?
- What factors should you consider when comparing one processor with another?
- What part of the processor compares?
- What's better Intel or AMD?
Most non-computer people only use the clock speed to compare two processors. This is a good comparison, but it is akin to comparing cars only by their top speed. There are many features of a car that are as important as rated speed. When comparing processors, many factors come into play. Larger cache and faster system bus speeds usually indicate more powerful processors. contrasts three powerful desktop processors.
RISC Processors
- What is an example of RISC?
- Is Apple m1 RISC or CISC?
- Is AMD RISC or CISC?
- Is Intel RISC or CISC?
- Is 8086 RISC or CISC?
- Is Intel i7 RISC or CISC?
The processors in IBM-compatible PCs are complex instruction set competing CISC processors. The instruction sets for these CPUs are large, typically containing 200 to 300 instructions.
Another theory in microprocessor design holds that if the instruction set for the CPU is kept small and simple, each instruction will execute in much less time, allowing the processor to complete more instructions during a given period, CPUs designed according to this theory are called reduced instruction set computing. (RISC) processors. RISC instruction sets are considerably smaller than those used by CISC processors. The RISC design, which is used in the PowerPC processor but was first implemented in the mid-1980s, results in a faster and less expensive processor.
Parallel Processing
- What would be an example of parallel processing?
- What does parallel processing mean in psychology?
- What is parallel computing with example?
- What is the difference between parallel processing and multiprocessing?
- What is parallel processing also called?
- What is parallel processing and its type?
Another school of thought on producing faster computers is to build them with more than one processor. This type of system is said to be a multiprocessing (MP) system. The result is a system that can handle a much greater flow of data, complete more tasks in a shorter time, and deal with the demands of many input and out- put devices.
A special form of MP that uses an even number of processors is symmetric multiprocessing (SMP). SMP's advantage is the number of processors is limited to a power of two. The limitation on the number of processors makes the systems easier to design. Parallel processing is not a new idea in the minicomputer, mainframe, and supercomputer arengs.Manufacturers have developed computers with hundreds or even thousands of microprocessors- systems known as massively parallel processing (MPP) computers. (RISC) processors. RISC instruction sets are considerably smaller than those used by CISC processors. The RISC design, which is used in the PowerPC processor but was first implemented in the mid-1980s, results in a faster and less expensive processor.
Computer HP Desktop
- How fast is fast enough?
- How powerful does a computer need to be?
We may never know the ultimate answer to these question because when it comes to computer performance, the bar continues to be raised. Software developers and users constantly make greater demands of computers, requiring them to perform an ever higher number of tasks. Processor developers respond with chips of ever increasing speed and power. Chipmakers such as Intel, IBM, Freescale, Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), and others keep proving that there seems to be no end to the potential power of the personai computer.
This lesson looks at the processors most commonly found in personal computers and describes some of their most important features and distinguishing characteristics. You will learn how these CPUs are typically differentiated from one another and see how their performance is measured. You also will learn some of the ways you can extend the power of your PC's processor to other components by using its expansion capabilities.

.png)


.png)





0 Comments